Oil sands ... uncertain future
Oil sands ... uncertain future
Global oil and gas exploration projects worth more than $150 billion are likely to be put on hold next year as plunging oil prices render them uneconomic, data shows, potentially curbing supplies by the end of the decade.
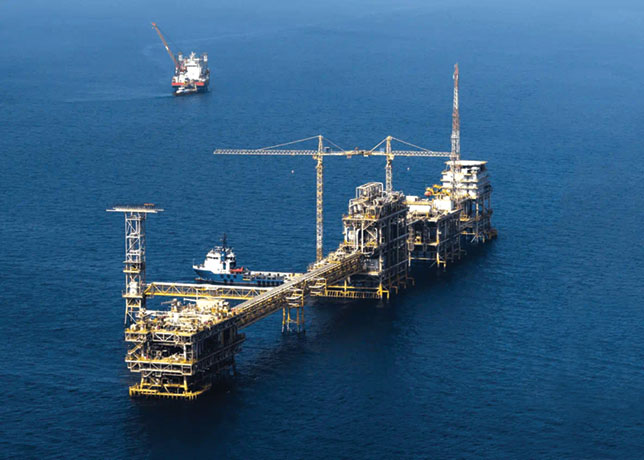
As big oil fields that were discovered decades ago begin to deplete, oil companies are trying to access more complex and hard to reach fields located in some cases deep under sea level. But at the same time, the cost of production has risen sharply given the rising cost of raw materials and the need for expensive new technology to reach the oil.
Now the outlook for onshore and offshore developments – from the Barents Sea to the Gulf of Mexico – looks as uncertain as the price of oil, which has plunged by 40 per cent in the last five months to around $70 a barrel.
Next year companies will make final investment decisions (FIDs) on a total of 800 oil and gas projects worth $500 billion and totalling nearly 60 billion barrels of oil equivalent, according to data from Norwegian consultancy Rystad Energy.
But with analysts forecasting oil to average $82.50 a barrel next year, around one third of the spending, or a fifth of the volume, is unlikely to be approved, head of analysis at Rystad Energy Per Magnus Nysveen said.
“At $70 a barrel, half of the overall volumes are at risk,” he said.
Around one third of the projects scheduled for FID in 2015 are so-called unconventional, where oil and gas are extracted using horizontal drilling, in what is known as fracking, or mining. Of those 20 billion barrels, around half are located in Canada’s oil sands and Venezuela’s tar sands, according to Nysveen.
Geographically, the projects on the balance are widespread.
Chevron’s North Sea Rosebank project is among those with a shaky future and a decision on whether to go ahead with it will likely be pushed late into 2015 as the company assesses its economics, analysts said.
This project was not deemed economic at $100 a barrel so at current levels it is clearly a no-go, said Bertrand Hodée, research analyst at Paris-Based Raymond James. He estimates a development cost of $10 billion for Rosebank, with potential reserves of 300 million barrels – meaning the Chevron would only recoup $33 a barrel.
Even with oil at $120 a barrel, the economics of some projects around the world were in doubt as development costs soared in recent years. Chevron’s Rosebank project has already been delayed for several years.
In response to a question from Reuters, the company said “the Rosebank project is in the Front End Engineering and Design phase. The review of the economics and the additional engineering work is progressing ... It is premature to make any statements on an FID date.”
Hodée said any offshore project with a development cost above $30 a barrel would most likely be put on hold in current oil prices.
Norway’s Statoil said it had postponed until next October – a six-month delay – a decision to invest $5.74 billion in the Snorre field in the Norwegian Sea as its profitability was under threat.